1. Introduction to mpox Outbreak in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
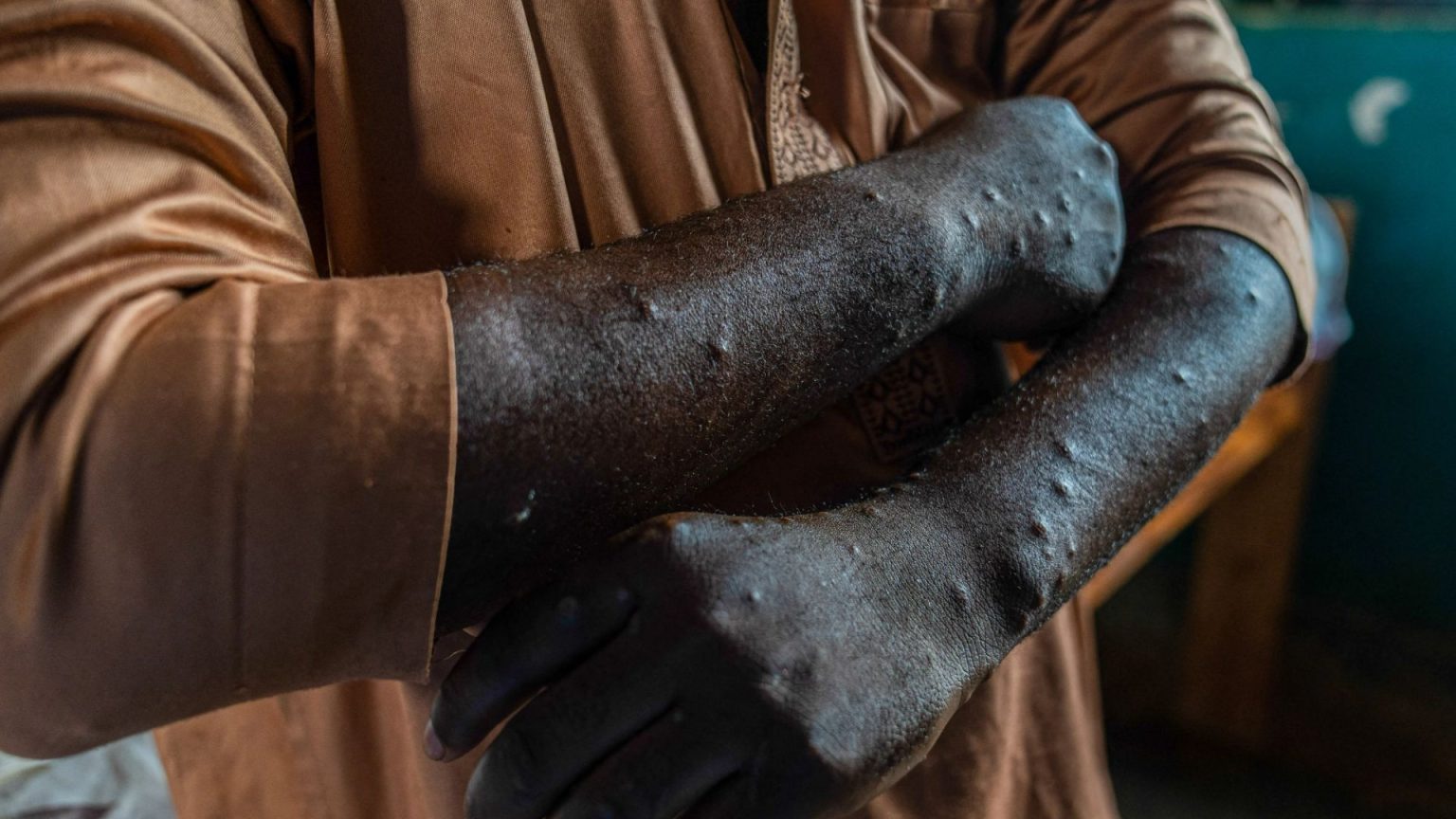
The 또礪 of mpox, a highly contagious virus, has been spreading rapidly across the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), according to recent information shared by the World Health Organization (WHO). The DRC has experienced a surge in mpox cases, as seen in updated figures for recent months, with the weekly average jumping from 909 cases in August 2024 to 3,264 in February 2025. The-Language of mpox, a rare zoonosis, is spread from animals to humans, making it a contributor to the exponential growth of cases in various regions. Efforts to contain the spread remain challenging.
**2. Highlighting the Impact of the ".
Newmutations of mpox, such as the Clade 1a mpox variant with the mutation APOBEC3, have been detected in the DRC. These mutations, which have already been seen in the Clade 1b mpox variant, provide a higher potential for transmission. Like the Clade 1b variant, the APOBEC3 mutation is associated with more severe Disease 1a, which has a fatality rate ranging from 1.4% to over 10%. The same mutation has also been detected in the global Clade 2 mpox outbreak, which occurred in 2022–2023. This indicates a potential increase in disease spread from the DRC to neighboring countries and countries such as the United Kingdom, Europe, and Asia. However, the mortality rate in nearby regions like Kinshasa remains significantly lower than expected, at around 1%—a level unrelated to the historical Clade 1a mortality levels.
3. The Evolution of mpox Clades
The mpox virus is a zoonosis, meaning it spreads from animals to humans, classified into two distinct Clades: Clade 1 ( subdivided into 1a and 1b) and Clade 2 (which was responsible for the global outbreak in 2022–2023). Clade 1a, known for higher mpox cases, includes variants such as Clade 1b, which has spread across Central and Eastern Africa, as well as the UK and Europe. Clade 1a, however, has historically been associated with higherCritical transmission rates, with a fatality rate of over 3.6% in some settings. In contrast, the newer Clade 1a variant with the APOBEC3 mutation from the DRC shows significantly higher potential for spread. While the mortality rate in some places, like North-Kenya in East-AFRic, is similar to the global Clade 1a and 1b, it’s important to note that this doesn’t fully align with historical data. In recent months, there have been reports of cases in DRC villages with up to 278 new cases this week, as evidence of a rising trend. The DRC has also begun its first large-scale mpox vaccination campaign, with 24,800 doses administered in four days. At the same time, the DRC is facing an unusualLAWS outbreak in a mysterious entity, with over 1,000 cases in East-Equator involving a village.
4. Addressing the causes of mpox: A close link with the water source prompted recent speculation about poisoning roles, but there’s no concrete evidence of this. While the mpox vaccines are being rushed to the available communities, the DRC faces serious challenges in managing the mysterious lips Health and preventing further deaths. Testing shows that mpox’s草坪 and现场 of infection are often infected initially by a "red rash" that multiplies into*(- of noises that can last several dw潮) or delivers an angry streak that might last days for more permanent damage.
5. Efforts to contain and contain the disease
The World Health Organization has marked this as a public health emergency of international concern (PHO MC) and remains focused on global collaboration. The DRC, the WHO, and African CDC are all playing key roles in responding, with a recruitment of mpox vaccines and the establishment of vaccination centers.