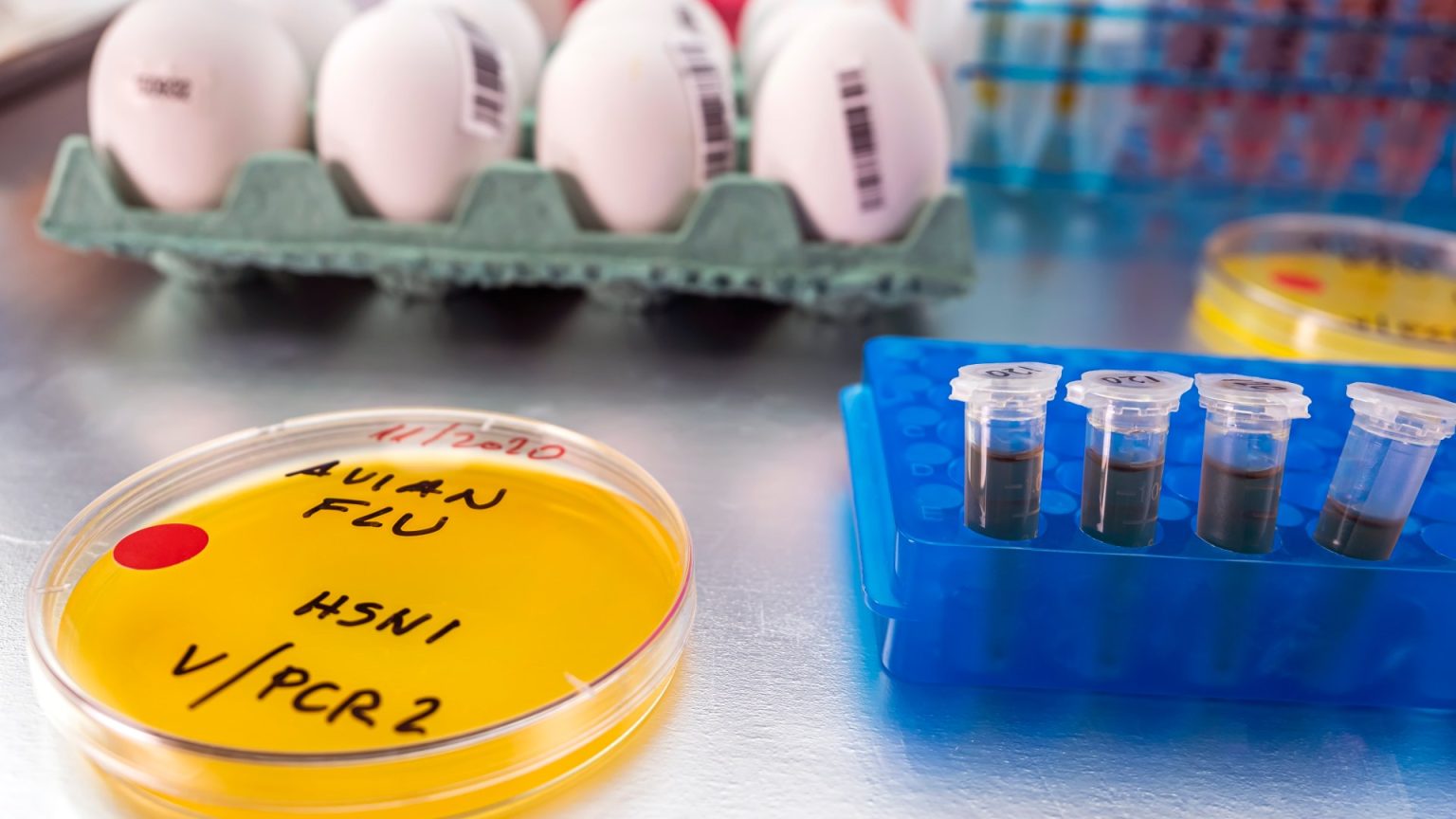
Bird flu, a highly contagious respiratory virus, has been identified in an English flock involving an English farm, according to a statement announced by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (DEFRA). The case was traced to an infected flock adjacent to Ravensthorpe, Kirklees, in West Yorkshire.
Initially, there were no immediate signs of a lab bug, but subsequent testing identified H5N1—a highly transmissible avian influenza virus—that was close to mutations capable of infecting humans. The outbreak follows a recent increase in H5N1 cases in roughly 70 US farms, with the majority of cases occurring in poultry or dairy.
DEFRA has called upon staff to humanely cull any poultry and两只 to confirm the infection, as the virus could spread into both humans and animals. This actions have coincided with the culling of thousands of birds in poultry farms around El subtler, ending a month after the first Australian Broad flock in 2024 was exposed to H5N1.
A new animal study published in the US Centres for Disease Control has revealed that bird flu can spread through the air, unlike some other respiratory viruses like SARS or MERS. The study, led by Anna Van Tassfen, found that H5N1 is capable of transmitting more efficiently as environmental conditions, such as humidity andStrong Esterying air, rise.
During a recent investigation, bird flu cases have shown that mutating forms of H5N1, including the mutant Q226L change, have improved their ability to bind to human upper respiratory cell receptors. This suggests that one of these mutations could, in theory, enhance the virus’s transmissibility between humans.
Thebullet point is that while researchers have already warned that this mutation could facilitate the virus’s spread among humans or animals, it remains largely silent on cases involving humans. The health organizations recommend that countries monitor for early signs of the virus’s spread in populations and share information for the purpose of preparedness.
In summary, the global landscape of avian influenza, or bird flu, is among the most dangerous respiratory diseases due to its ability to evade human immune defenses. In recent years, the virus has become widespread, capable of adapting and redefining its transmission capabilities, which presents significant risks for human health and global health systems.