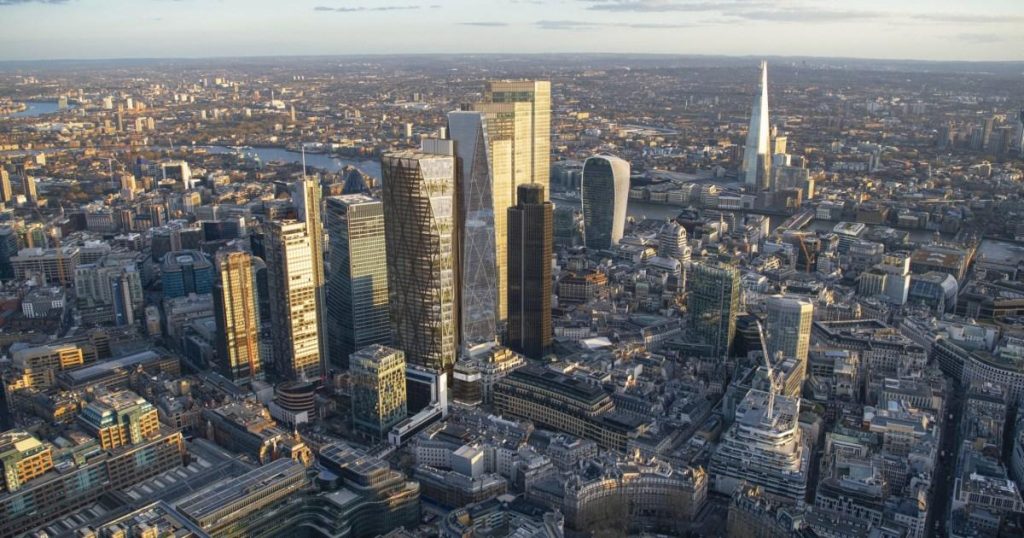
A new 54-story skyscraper, 99 Bishopsgate, is poised to reshape the London skyline, following the approval of its planning permission despite facing considerable opposition. Located near Liverpool Street Station, the colossal structure will introduce nearly 100,000 square meters of office space to the city. While proponents tout its economic benefits and architectural significance, critics, including former Archbishop of Canterbury Lord Rowan William, express concerns about its impact on the surrounding environment and historic structures. The ongoing debate highlights the complex considerations surrounding urban development and the delicate balance between progress and preservation.
The towering edifice, set to become a landmark addition to the City of London’s iconic skyline, joins the ranks of architectural giants like the Natwest Tower, the Gherkin, and Heron Tower. Its imposing height and modern design promise to transform the cityscape, yet this transformation comes at a cost. Concerns have been raised about the potential disruption to nearby historical sites, particularly the Grade I listed St Ethelburga’s Centre. The potential loss of natural light and the anticipated disruption during construction have fueled the opposition, leading some to label the project as “wholly undesirable.”
Despite these objections, Brookfield Properties, the developers behind 99 Bishopsgate, emphasize the project’s significant economic contributions. Dan Scanlon, President of Brookfield Properties, champions the building as “transformational” for London, highlighting the over £40 million in Community Infrastructure Levy (CIL) payments it will generate. This financial injection into the city’s infrastructure is seen as a key benefit, bolstering public services and contributing to the overall development of the area. The anticipated influx of businesses and the creation of numerous jobs further solidify the proponents’ arguments in favor of the project.
99 Bishopsgate is not merely an office block; it aims to be a destination in its own right. The inclusion of a free public viewing gallery and a restaurant offers a unique opportunity for visitors to experience London from a breathtaking perspective. This public amenity aims to integrate the skyscraper into the fabric of the city, providing a space for both residents and tourists to appreciate the sweeping views and engage with the building beyond its commercial function. The integration of these features is a strategic move to address concerns about the building’s potential exclusivity and inaccessibility to the general public.
However, the project’s sheer scale has presented unique challenges. The tower’s initial height had to be reduced to avoid interference with flight paths from London City Airport, a testament to the intricate planning required for such ambitious projects. The Civil Aviation Authority’s involvement underscores the importance of considering the broader impact on air traffic and safety regulations when constructing such tall structures in urban environments. This modification to the original design highlights the compromises that are sometimes necessary to balance architectural aspirations with practical considerations.
The debate surrounding 99 Bishopsgate reflects the broader tension between progress and preservation in urban development. While the building promises economic benefits and a modern architectural statement, it also raises concerns about the potential impact on historical sites and the surrounding environment. The ongoing discussion underscores the complex considerations involved in shaping the future of our cities, ensuring that development complements and respects the existing urban fabric. The project’s approval, despite the objections, signifies a decision to prioritize economic growth and architectural innovation, while also acknowledging the need to mitigate potential negative impacts. The implementation of 99 Bishopsgate marks a significant chapter in London’s ongoing architectural evolution, leaving a permanent mark on the city’s skyline and contributing to the ongoing dialogue about the future of urban spaces.