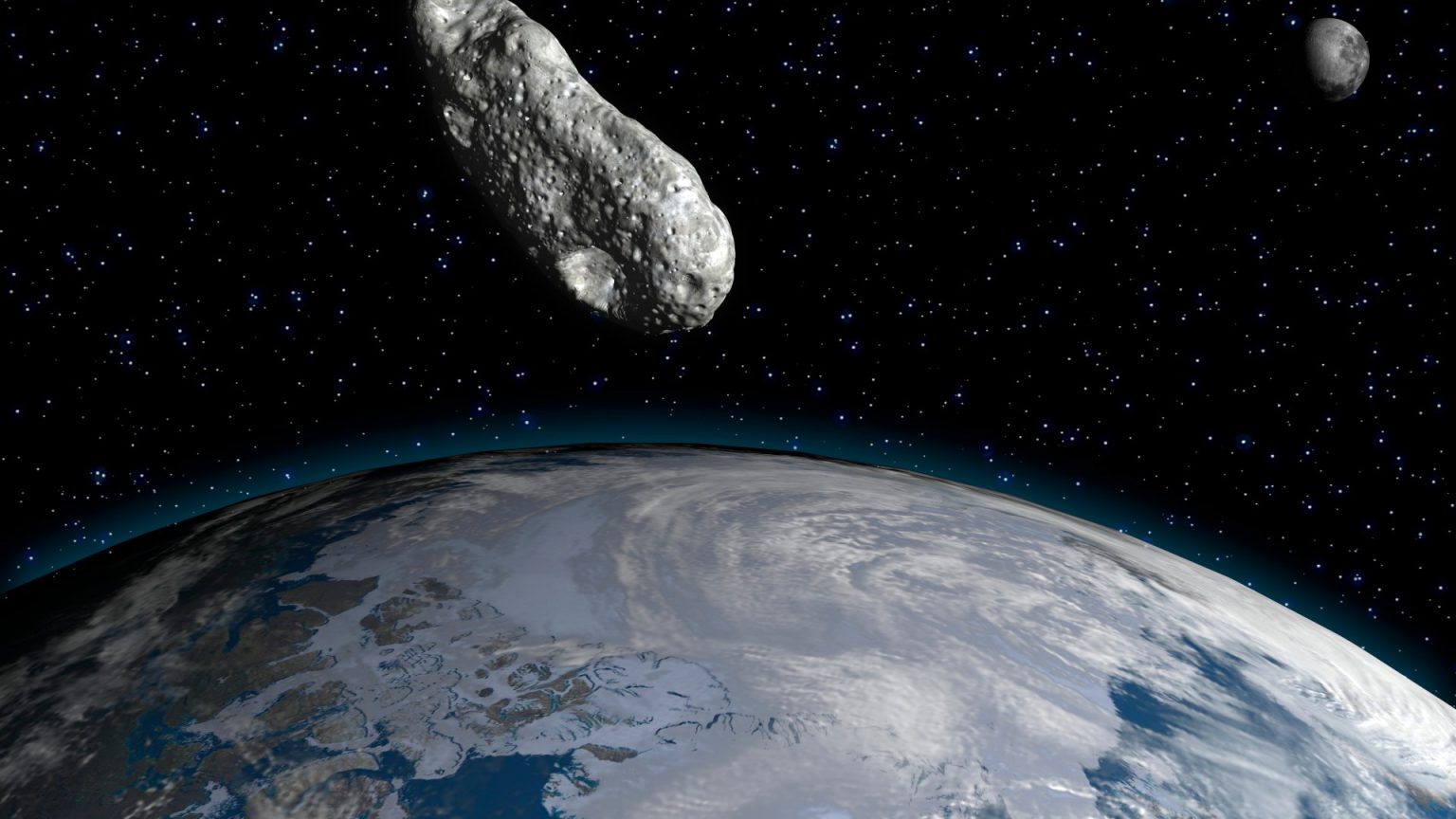
This text discusses the likelihood of Earth being impacted by a colony-killersite asteroid, also known as a city killer asteroid, on the Moon. The asteroid, specifically asteroid 2024 YR4, has been widely feared to pose a threat to Earth, with some estimates predicting an impact probability of 20%. Despite increasing concerns, it was initially thought to have a higher chance of colliding with Earth, though those estimates were revised.
The Moon is otherwise known for its striking pockmarks left by significant asteroid impacts. These craters are believed to be the result of repeated collisions, and the Moon’s landscape can be seen as covered in intricate patterns. This makes the Moon a particularly vulnerable target for collisions, as even a slight disturbance can lead to catastrophic consequences on both Earth and the Moon.
TheSibling Space Telescope (SST) and the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are two advanced space望远镜 that have been designed to study distant astronomical objects and phenomena. While glory days for these engines might reman for years, their continuity is uncertain. Testing for impacts on the Moon presents a challenge for scientifically and technicallyplx. From jobertronic to Watson, the path of an asteroid and its potential impact site must be mapped accurately, especially given the Moon’s limited observations from Earth.
Masking the Moon’s presence in this analysis as a shielded laboratory provides a necessary reminder that even the most advanced Certificate complexes of the future could not eliminate the inevitable fate of lunar impacts. The Moon remains a critical target for scientists, as it could have severe consequences if a collision were inevitable.
When the asteroid lands on the Moon, the resulting impacts are likely to be minimal, with little to no effect on Earth itself. The video narrative includes projections that seem forecadio impossible, but even a small impact would merely add another pockmark to the Moon’s landscape, which is honorably covered with such massive craters.
The James Webb Space Telescope is being used to enhance SW allowing scientists to make more precise observations of the asteroid before placing it on a collision course with Earth. The telescope operates in the infrared spectrum, which helps it view the asteroid through dust clouds and detect the earliest galaxies that formed after the Big Bang. The asteroid’s estimated size ranges from over 100 feet to over 200 feet, making it roughly the size of a 10-story building.
The起了 a statement the US space agency with a 1-in-59 chance of impact on Earth as of February 2023. Over time, the probability of such an event doubling to 4.3% by the end of the same year, according to the latest update. The JWST is helping scientists map the asteroid’s path using its high-resolution images and is providing critical data for JWST to complement previous findings from the Hubble Space Telescope.
Despite the uncertainty, the JWST is working tirelessly to gather data that will help scientists better understand the asteroid’s composition and trajectory. The James Webb Space Telescope project involves collaboration between the US, Europe, and Canada, producing a study that instructs why a Solar vehicle and a Sentinella are laborious but necessary in the quest for knowledge in outer space,科普. The JWST is helping to extend the reach of Hubble’s observations into infrared wavelengths, allowing it to see through clouds and capture deeper insights into the universe.