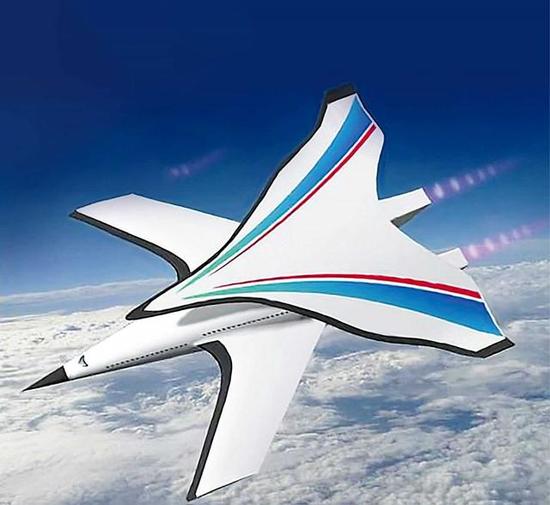
The pursuit of hypersonic passenger travel has taken a significant leap forward with the revelation of a Chinese experimental aircraft achieving a speed of over 5,000 mph (Mach 6.56) during a test flight. This breakthrough, spearheaded by Cui Kai, signifies a potential revolution in air travel, envisioning journeys from Beijing to New York in a mere two hours, a stark contrast to the current 12-14 hour duration. The project, initially met with skepticism, showcases a novel design featuring a rounded fuselage and cape-like wings, strategically engineered to convert downward pressure at high speeds into upward lift, a pivotal advancement in aeronautical engineering. This innovative approach addresses the limitations of internal space plaguing existing hypersonic aircraft, which have primarily been confined to military applications like missiles and unmanned reconnaissance. The test flight, conducted in August 2021 at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Centre, remained undisclosed until recently, underscoring the sensitive nature of this cutting-edge technology.
The successful test represents a monumental stride towards realizing the dream of global travel within an hour, a concept once dismissed as fanciful. Cui Kai’s unwavering belief in innovation amidst doubt propelled the project forward, culminating in the exhilarating moment the prototype soared into the sky, marking a profound sense of achievement. The aircraft’s unique design not only tackles the speed barrier but also addresses the critical issue of limited passenger and cargo capacity that has hampered the development of hypersonic commercial aircraft. The broad wing configuration, while complex, ingeniously transforms a significant aerodynamic challenge into an advantage, paving the way for future hypersonic aircraft to potentially match the capacity of today’s jumbo jets. This signifies a paradigm shift in the aviation industry, moving beyond purely military applications of hypersonic technology to the realm of commercial passenger transport.
However, the path to realizing this ambitious vision is fraught with challenges. Despite the successful test flight, Cui Kai acknowledges the significant hurdles ahead, primarily concerning power systems, materials science, and structural integrity. The project is still in its early stages, requiring further research and development to overcome these technical obstacles. The high cost and complexity of hypersonic technology are evident in the numerous tests conducted, each costing hundreds of thousands of yuan. Furthermore, the project faces competition from other nations, particularly the United States, which is also actively pursuing hypersonic aircraft development, including the SR-72 “Darkstar” with its projected Mach 6.0 speed. This international race underscores the strategic importance of hypersonic technology and the potential for global leadership in this emerging field.
The endeavor also carries the weight of past failures in supersonic aviation, most notably the Concorde. This iconic aircraft, while a marvel of engineering, ultimately succumbed to a combination of factors, including high development costs, operational limitations, and a fatal crash that eroded public confidence. The Concorde’s experience serves as a sobering reminder of the immense challenges involved in developing safe and commercially viable supersonic and hypersonic aircraft. Overcoming these challenges requires meticulous attention to safety, robust engineering solutions, and addressing public concerns regarding the environmental impact and economic viability of such technology. The Chinese project must learn from the Concorde’s shortcomings to ensure the safety and long-term success of its hypersonic ambitions.
The parallels between the Chinese project and the Concorde are striking, highlighting the complex interplay of technological ambition, economic realities, and public perception. Both projects represent significant leaps in aviation technology, pushing the boundaries of speed and challenging conventional notions of air travel. However, the Concorde’s eventual demise underscores the importance of not only achieving technological breakthroughs but also ensuring their sustainability and safety. The Chinese project must navigate these complex considerations to avoid repeating the Concorde’s fate. This includes careful consideration of engine design, material selection, and addressing the inherent challenges of high-speed flight, such as overheating and structural stress. Furthermore, public acceptance will be crucial, requiring transparency about safety protocols, environmental impact, and the long-term economic viability of hypersonic travel.
The Chinese team remains tight-lipped about the next phases of development, including the existence or construction of a full-scale model and the timeline for its maiden flight. The secrecy surrounding these crucial details underscores the competitive landscape of hypersonic technology development. While the successful test flight represents a significant achievement, the road ahead remains long and arduous. Continued investment, relentless innovation, and meticulous attention to safety will be paramount to realizing the dream of routine hypersonic passenger travel. The Chinese project, while promising, must also grapple with the legacy of the Concorde, learning from its triumphs and failures to ensure the ultimate success of this ambitious endeavor. The future of hypersonic flight hinges on addressing the technical, economic, and safety challenges that have plagued previous attempts to conquer the speed barrier.