2025: A Year of Ambitious Space Endeavors
The year 2025 promises to be a pivotal one for space exploration, marked by a diverse array of missions pushing the boundaries of human ingenuity and scientific discovery. From asteroid sampling to private space stations and lunar surface exploration, the coming year is poised to witness significant advancements in our understanding of the cosmos and our place within it. China’s Tianwen-2 mission, targeting the near-Earth asteroid Kamoʻoalewa, stands out as a particularly ambitious undertaking. Scientists believe this asteroid may be a fragment of our own Moon, and the mission aims to collect samples for analysis back on Earth. Following this initial phase, the Tianwen-2 spacecraft will leverage Earth’s gravity for a slingshot maneuver towards the main-belt comet 311P/PANSTARRS, arriving in the mid-2030s, further expanding our knowledge of celestial bodies.
The lunar surface will also be a focal point of exploration in 2025. Building upon the successful Odysseus Moon landing in 2024, NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program will continue to deploy commercial landers to the Moon. Companies such as Astrobotic, Intuitive Machines, and Firefly Aerospace are scheduled to deliver payloads designed for diverse scientific investigations. These missions will delve into lunar geology, test cutting-edge technologies for future human missions, and collect crucial data on the Moon’s environment. The information gathered will be instrumental in paving the way for a sustained human presence on our celestial neighbor.
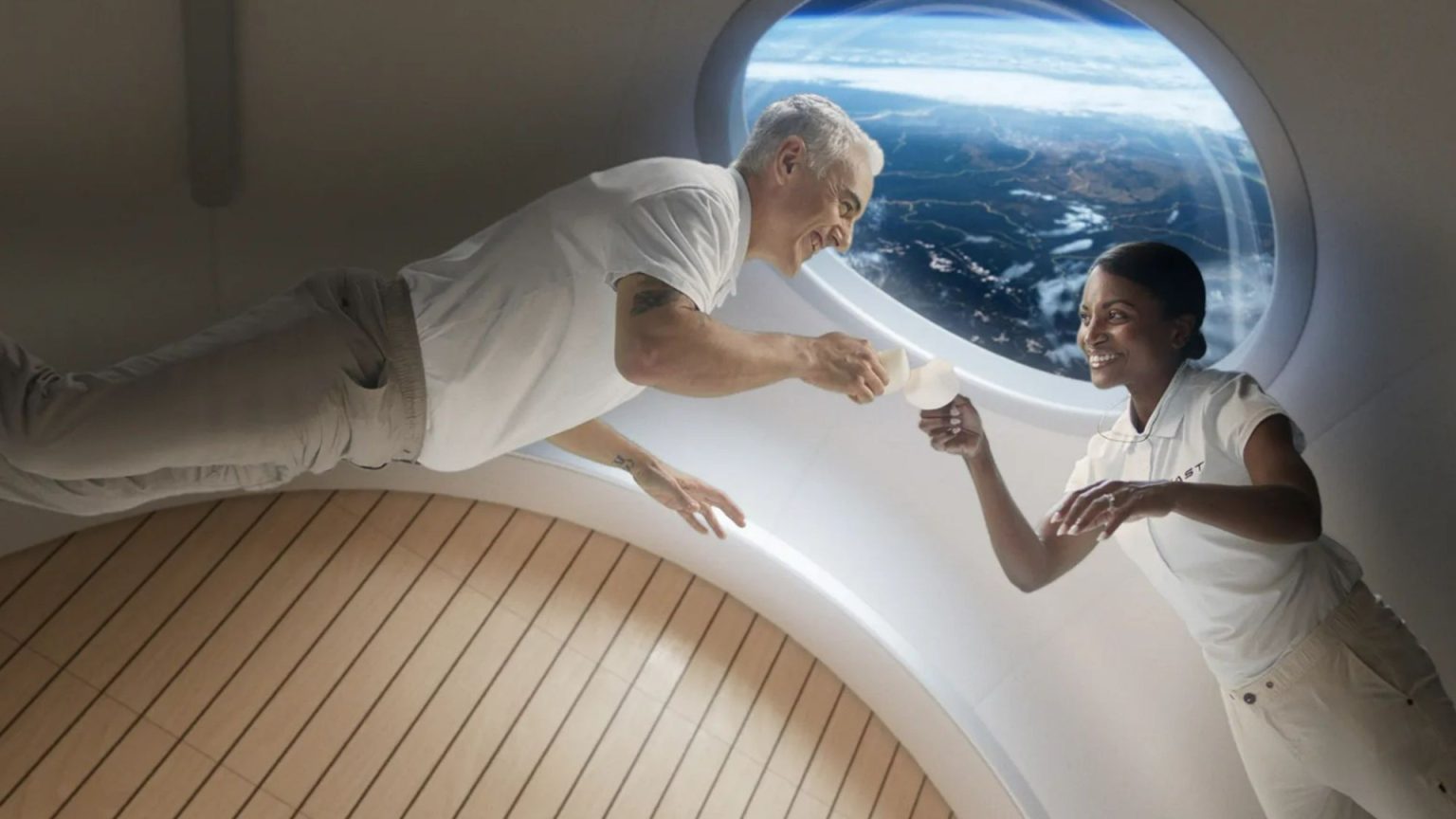
Beyond lunar exploration, 2025 will witness a significant step towards the commercialization of space with the launch of Haven-1, the world’s first commercial crewed space station. Developed by the private space company Vast, Haven-1 promises a luxurious and technologically advanced orbital experience, featuring amenities such as a gym, private rooms, and high-tech research facilities. This venture represents a significant shift in the landscape of space exploration, opening up new possibilities for both scientific research and space tourism.
As Haven-1 prepares for launch, the International Space Station (ISS), a long-serving symbol of international collaboration in space, is nearing the end of its operational life. NASA plans to de-orbit the ISS in 2031, culminating in a controlled descent into Point Nemo, a remote area in the Pacific Ocean designated as a "space graveyard." This marks the end of an era for the ISS, which has hosted hundreds of astronauts and space tourists over its decades of service, and underscores the evolving nature of space exploration.
The European Space Agency (ESA) is also poised to make significant strides in 2025 with the orbital test flight of its uncrewed Space Rider spaceplane. Designed for scientific experiments in low Earth orbit, Space Rider will investigate the behavior of plants and materials in microgravity, as well as test crucial technologies for future missions to the Moon and Mars. This includes advanced telecommunication systems and robotic exploration tools, essential for long-duration space travel and surface exploration.
Finally, SpaceX, under the leadership of Elon Musk, is gearing up for a groundbreaking test of its Starship spacecraft, involving the transfer of fuel between two Starship vehicles docked in low Earth orbit. This in-orbit refueling capability is critical for Starship’s ambitious long-term goals of transporting humans to Mars and potentially beyond. The successful demonstration of this technology would represent a significant leap forward in our ability to conduct complex operations in deep space.
In summary, 2025 promises to be a year of remarkable progress in space exploration. From asteroid sampling and lunar landings to the launch of a private space station and the testing of advanced spacecraft technologies, these missions represent not only significant scientific endeavors but also a testament to human ambition and our enduring fascination with the cosmos. The insights gained from these missions will undoubtedly shape the future of space exploration and broaden our understanding of the universe around us.