The Health Alert Regarding Skin C Removal Wipes and the Breakthrough in the UK Healthsecurity Agency’s Investigation
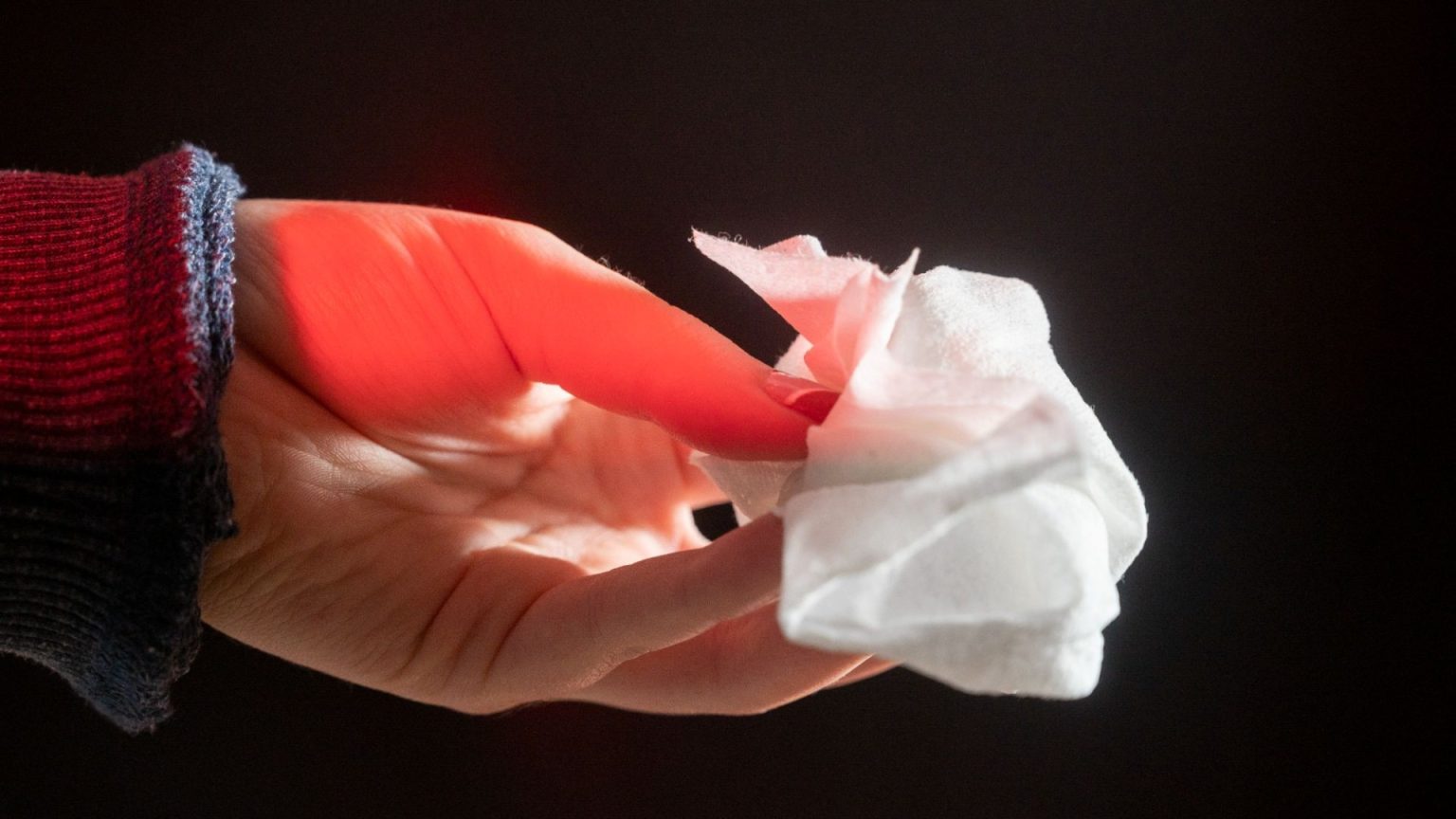
In recent weeks, the UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has revealed significant developments regarding the use of skin cleansing wipes contaminated with life-threatening bacteria. A study involving 35,000 to 50,000 people in the UK has emerged, confirming cases of infections linked to Burkholderia stabilis, a bacteria that causes severe bacterial infections. The findings indicate that non-sterile wipes, including ValueAid Alcohol Free Cleansming Wipes, Steroplast Sterowipe Alcohol Free Cleansing Wipes, and Reliwipe Alcohol Free Cleansing Wipes, have been identified as transmitting the bug. The UKHSA has undone the old belief that using these wipes could cause infections, warning that their use may inadvertently transmit the bacteria, which is thriving in natural environments and not found in healthy individuals.
To prevent further spread, the health authorities have issued a press release calling upon individuals and healthcare professionals to act swiftly. It is crucial not to use these contaminated wipes for any purpose, including treating broken skin, wounds, or any actions that could result in infection. Parents and caregivers should also report any symptoms they’ve experienced, including redness, swelling, symptoms of an infection in any manner, and possible fever or chills.
These findings are a concerning reminder of the need for vigilance and clear guidelines. As a director of the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), Alison Cave emphasized, it is paramount that healthcare professionals do not distribute, market, or use any wipes marked as ‘sterile’, as chlorine is essential for eliminating germs. Non-sterile, alcohol-free wipes should only be used on well- Inspection.
The UKHSA also introduced an ‘Aewsmt Alert’ to prompt healthcare workers to ensure that any contaminated wipes used in patient care are thoroughly tested and discarded or properly disposed of. This serves as a reminder that each action, even small, can have significant consequences in public health.
In conclusion, with the necessary measures in place, the risk of infection linked to the use of these contaminated wipes is minimized. A proactive approach to eliminating these contaminated products and ensuring proper disposal will help protect individuals and the health of all. Preparation for the known contamination should lead to safer decisions, emphasizing that even the smallest actions can only be taken with intention to protect all concerned parties.