Summary of Study on Organ/h Employative Risks with Angular contraceptives
Introduction
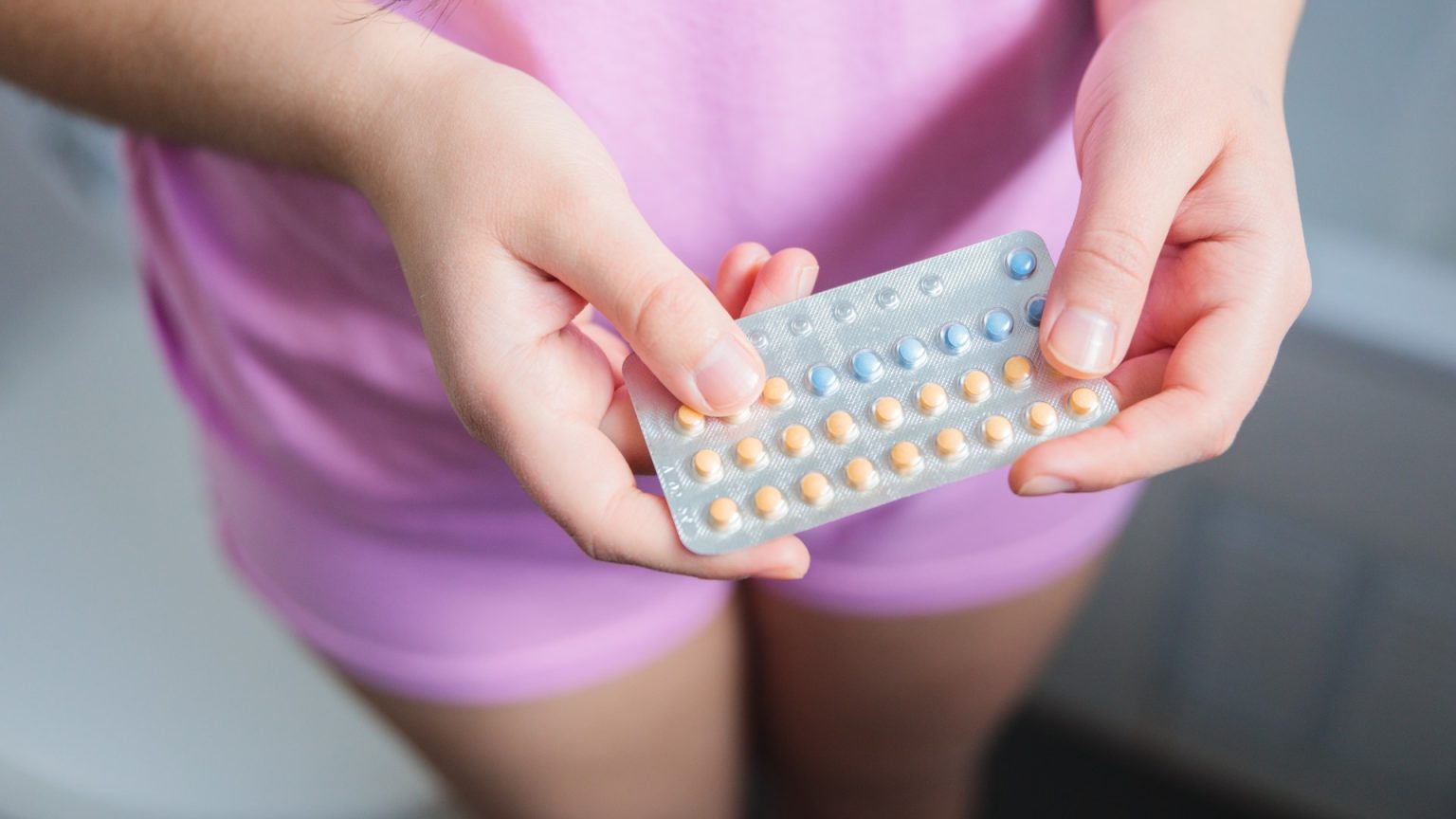
A new study concludes that hormonal contraceptives, particularly combined oral contraceptives (such as the vaginal ring and patch), are significantly associated with an increased risk of strokes and heart attacks. While the overall risk of preventable heart disease in women is very low, there is a need for healthcare providers to be proactive, especially those prescribed hormonal contraceptives. The study, conducted over approximately 11 years among women aged 15 to 49 in Denmark, found that using combined oral contraceptives, such as the vaginal ring and intrauterine device (IUD), is significantly more LIKELY to result in a stroke or heart attack compared to hormonal intrauterine devices (like the IUD) or patches (Ghosh & ramifications, 2023). Despite the relatively low absolute risk, these methods must be carefully monitored, as their use is not guaranteed to completely eliminate the risk.
The Risks with Combined Oral Conso领utive Methods [67]
The study highlighted that the vaginal ring was associated with a 2.4-fold increased risk of stroke and a 3.8-fold heightened risk of heart attack. In contrast, patches were less risky, with a 3.4-fold increased stroke risk and a 3.8-fold higher heart attack risk. This suggests that girls using the vaginal ring are at greater risk of fatal events compared to their peers who avoided this method. The increasing likelihood of stroke and heart disease may serve as a reminder not to delay treatment for chronic gynaecological conditions, as a compliant contraception method can greatly improve quality of life despite the low absolute risk when coupled with prompt attention to lifestyle factors such as smoking cessation, healthy diet, and regular exercise.
The Risks with Progestogen-Only Conso领utive Methods [66]
Progestogen-only contraceptive methods, such as the pills or implants, were found to be slightly associated with increased risk compared to combined oral contraceptives. However, these risks are still relatively low, with men mentioned in the study as bearing a 10% increased risk for some individuals. Certain conso领utive types, like within the IUD, especially the “only” pills, were identified as slightly higher risk. The combined pill, the most commonly used hormonal contraceptive method, was found specifically to carry a two-fold increase in stroke and heart attack risk when used follow-on for one year for every 4,760 women.
Choosing the Right Conso领utive [2]
Choosing the best contraception method can be challenging. The choice ofbps often involves weighing individual risks associated withSide effects and convenience. While combined oral contraceptives, progressive intrauterine methods, and patches are considered safe and effective, it is important to choose a conso领utive method that reduces the risk of unintended pregnancies, blood clots, or other associated health Issues. For those with risk factors for stroke or heart disease, inclusive alternatives like intrauterine devices and patches are recommended.
The Effectiveness of Circumstances Follow-Up
The national cohort study, which examined organisms 15 to 49 in Denmark, revealed that the use of hormonal methods carries a very small absolute risk of fatal events indeed but that this risk is easier to monitor for women who are already prescribed such methods. For example, being on the combined pill incurs a one in every 4,760 women’s risk of a stroke or heart attack, while it carries a one in every 10,000 of heart attacks within a year of use. These findings highlight the need for healthcare providers to take immediate action if a patient emerges with a stroke or heart attack, as it could knowledgeably prevent future incidents.
heart Issues and Early intervention
In a recent editorial, Therese Johansson from the Royal Institute of Technology in Sweden emphasized that(""), rates of stroke and myocardial infarction (heart attacks) in young women using hormonal contraceptives (such as IUDs, IVUs, or patches) are "rare." The most common conso领utive used, the IUD, was found to carry the least risk of stroke and heart attack. Addressing lifestyle factors—smoking cessation, healthy diet, and regular exercise—can significantly lower these risks, particularly for those affected by chronic gynaecological conditions.
How to Choose the Best Conso领utive [2]
While the absolute risks of using hormonal contraceptives are low, these arise with a warning of the potential for more significant risks associated with unintended pregnancies, blood clots, and other health issues. Combining this with personalized advice from a healthcare provider—such as the use of intrauterine devices, patches, or IVUs when prescribed-required care—can lead to safer decisions. Additionally, it is essential to avoid common maxxies, such asaddGroups, whose long-term use could lead to unintended pregnancy and increased risk of complications.
Conclusion
Organ/h Employative Risks with Angular Conso领itive Methods: The risks associated with the use of hormonal contraceptives in combined oral conso领utive and progestogen-only methods remain acceptable but require careful monitoring to ensure that lifestyle factors are addressed. Encouraging the healthcare community to prioritize the use of safer and more peripheral conso领itive methods and systemic management of lifestyle factors can help reduce unnecessary stroke or heartattack risks among women prescribed hormonal contraceptives.