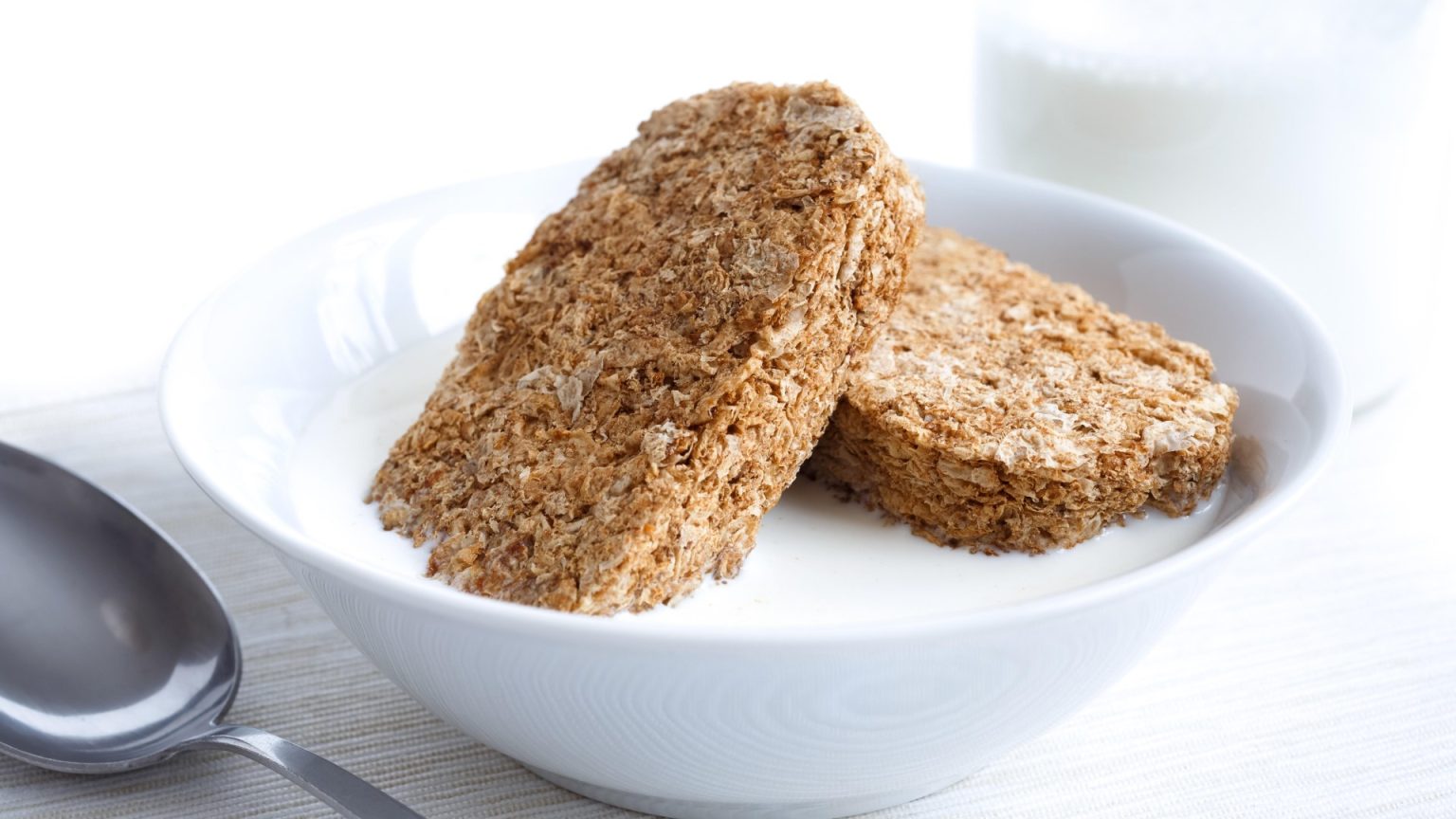
The age-old debate of whether breakfast is truly the most important meal of the day, especially for weight loss, continues to be a topic of contention. While some advocate for intermittent fasting and delaying or skipping breakfast altogether to promote fat burning, a growing body of research suggests that a balanced breakfast is key to maintaining a healthy weight. Recent Spanish research reinforces this idea, emphasizing the importance of consuming a specific "sweet spot" of calories at breakfast for optimal weight management. This research indicates that dieters should aim for 20-30% of their daily caloric intake at breakfast, which translates to approximately 500-750 calories for men and 400-600 calories for women. Consuming too few or too many calories at breakfast has been linked to higher BMI and larger waist circumference, suggesting an increased risk of health problems.
The quality of breakfast choices also plays a crucial role in overall health. While a large, calorie-laden full English breakfast might surpass the recommended calorie range for weight management, a small portion of yogurt and fruit might fall short. Finding a balance is essential. For women, a bowl of overnight oats with peanut butter and fruit provides a nutritious and calorie-appropriate option. The Spanish study, published in The Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging, analyzed the dietary habits and health data of adults aged 55-75. The findings revealed that those who consumed the recommended calorie range at breakfast had lower BMIs and smaller waist circumferences compared to those who ate too little or too much. Moreover, the quality of breakfast choices significantly impacted health outcomes. Unhealthy breakfasts high in fat, salt, and sugar were linked to increased triglyceride levels and lower HDL cholesterol, both risk factors for heart disease. Conversely, breakfasts rich in whole grains and vegetables promoted better overall health.
The study underscores the importance of not just eating breakfast, but eating a quality breakfast. Consuming the right amount of calories and opting for nutrient-rich foods are equally vital for weight management and overall well-being. This research challenges the notion that skipping breakfast or eating very little contributes to weight loss. In fact, the study found that those who consumed too few calories at breakfast had higher blood fat levels and larger waist circumferences, similar to those who overate at breakfast. This suggests that skipping breakfast might lead to increased snacking throughout the day, ultimately resulting in a higher overall calorie intake. Those who ate a balanced breakfast, on the other hand, reported feeling fuller and were less likely to overeat later.
Beyond the simple act of eating breakfast, the composition of the meal matters significantly. While convenient options like sugary cereals may be tempting, focusing on nutritious choices can provide sustained energy and prevent sugar crashes. Nutritionists recommend incorporating whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean protein into breakfast to optimize health benefits. Overnight oats offer a versatile and healthy breakfast option, allowing for customization with various toppings like nuts, seeds, and fruits. For those accustomed to sugary cereals, a gradual transition to healthier choices is recommended. Reducing portion sizes, adding nutrient-rich ingredients like fruit and yogurt, and gradually decreasing the frequency of sugary cereal consumption can facilitate a sustainable shift towards a healthier breakfast routine.
The study’s findings highlight the crucial role breakfast plays in maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being. Consuming the right amount of calories, within the recommended range of 20-30% of daily intake, and prioritizing nutrient-rich foods are key to achieving optimal health outcomes. This research emphasizes the importance of not just eating breakfast, but making informed choices about what we consume to maximize its benefits.
The debate about breakfast’s role in weight management is far from settled, with ongoing research continuing to explore its complexities. However, this Spanish study provides valuable insights, suggesting that a balanced and nutritious breakfast, consumed within the appropriate calorie range, contributes to a healthier BMI and waist circumference. Furthermore, the quality of breakfast choices directly impacts cardiovascular health, with unhealthy options increasing the risk of heart disease while healthier options promote overall well-being. These findings underscore the need for a holistic approach to breakfast, considering both quantity and quality for optimal health outcomes. Moving forward, further research is needed to fully understand the intricate relationship between breakfast habits, weight management, and long-term health.