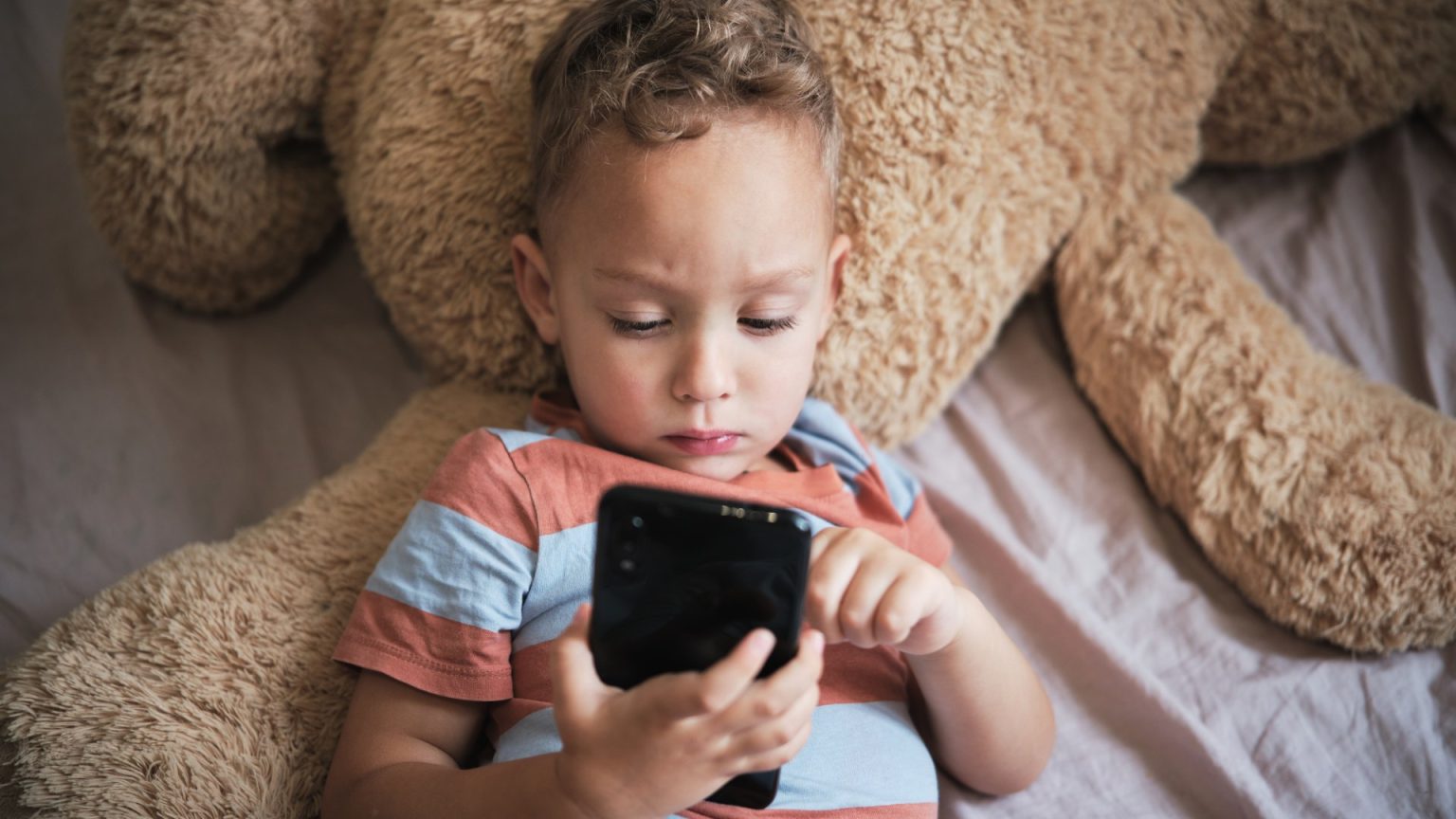
A Study Highlights the Link Between Screen Time and Heart ATTACK Risks in Teenagers and Young Adults
In recent years, the rise in excessive screen time has been correlate with an increased risk of cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and strokes. A study published in The American Heart Association Journal, which analyzed data from 1,000 participants across Denmark, revealed a strong correlation between excessive screen time and cardiometabolic risks. The findings indicate that individuals who slept fewer hours per night are at a greater risk of developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance. This study underscores the critical role of screen time in increasing cardiovascular risks, particularly in younger generations.
The Research Highlights the Importance of Sleep as a Regulator of Heart Disease Risks
One key insight from the study is that sleep habits play a significant role in mitigating these risks. Participants who slept fewer hours were found to be at greater odds with high blood pressure, elevated blood cholesterol levels, and insulin resistance, compared to those who slept more hours. This suggests that reduced sleep could indirectly compensate for the increased risk of cardiovascular events caused by excessive screen time. The study’s findings highlight the importance of maintaining a balance between screen time and sleep habits to reduce cardiovascular and heart disease risk.
The Role of Screen Time in Heart and Metabolic Risks
Excessive screen time is not only linked to medical risks but also poses significant lifestyle implications for heart health. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance are some of the primary contributors to these risks, and these factors directly impact heart health. Regular exercise, a well-known strategy to reduce cardiovascular risks, is even more critical when screen time is the primary form of entertainment in the household. For example, adults who spend three or six hours a day on screens are at a slightly higher risk of cardiovascular issues compared to those who engage in more engaging activities.
The Complications of Poor Sleep Habits
While most research focuses on the correlation between screen time and medical risks, the study also emphasizes the role of sleep in exacerbating cardiovascular and metabolic health issues. Sleep is crucial for sleep intact development, including good sleep hygiene, a sufficient resting heart rate, and adequate sleep duration. Disasters such as poor sleep can lead to negative mental health outcomes, increased stress levels, and potential cardiovascular risks, empowering individuals to consider sleep as a critical component of their overall health regimen. Misaligned sleep schedules can also amplify the negative impacts of excessive screen time on heart health.
Screen Time as a Distraction, Not a Solution
Screen time, while convenient, can be a significant distraction from more meaningful activities like exercise, family interactions, and mental health. This suggests that excessive screen time is not only costly to individuals but also potentially harmful long-term. It can lead to unhealthy habits, such as spending time in front of screens when not currently engaged in vital activities that improve physical and mental well-being. Over time, this can lead to more significant harm to cardiovascular and metabolic health, highlighting the need for a more ethical approach to screen time habits.
The Need for Early Intervention
The importance of early intervention cannot be overstated. As noted, many of these findings were derived from studies conducted with young participants. This underscores the need for earlier intervention programs to identify individuals at risk of cardiovascular events and facilitate changes in screen habits. Early identification of risk factors allows for more targeted and effective approaches to reducing these issues, ultimately promoting a healthier future for both families and individuals.
Lifestyle Changes: Beyond Screen Time
Beyond excessive screen time, other lifestyle factors play a significant role in cardiometabolic risks. Regular physical activity—such as walking, biking, or tennis—removes sedentary behavior and improves heart health. Similarly, diets rich in nutrients, including lean proteins and healthy fats, can counteract the effects of high blood pressure and contribute to metabolic health. In addition, effective moderation of blood sugar levels is crucial for managing heart disease risk. Stress management is another pillar of preventive care, with practices like exercise, meditation, and engaging in meaningful time spent with loved ones proving to be particularly effective.
The Consequences of Overrightarrow Screen Play in Everyone
Moreover, screen time is a habit that can be inherited and influenced by family members.suggesting that involving other family members, like relatives or even friends, can be a valuable tool for setting new habits and modeling healthy behaviors. Additionally, engaging in enjoyable activities, such as sports, puzzles, or creativity, can complement screen time without increasing emotional depletion or negative impacts.
In summary: Implementing Healthy Habits, Screen-Time Constraints, andaved Outcomes
The scientific findings of this study underscore the importance of adopting healthy lifestyles as a tool to protect against pitfalls like heart disease and stroke. Screen time habits, while convenient and currently unavailable, play an inevitable role in raising cardiovascular and metabolic risks, particularly early in life. By setting clear limits on screen time, understanding Sleep patterns, and adopting behaviorally rebalanced practices, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and stroke while also promoting a more balanced and healthier way of living. These insights are not only valuable for young adults but also have broad implications for all of life, reminding us that screen time starts early and has a long-term impact on our health.