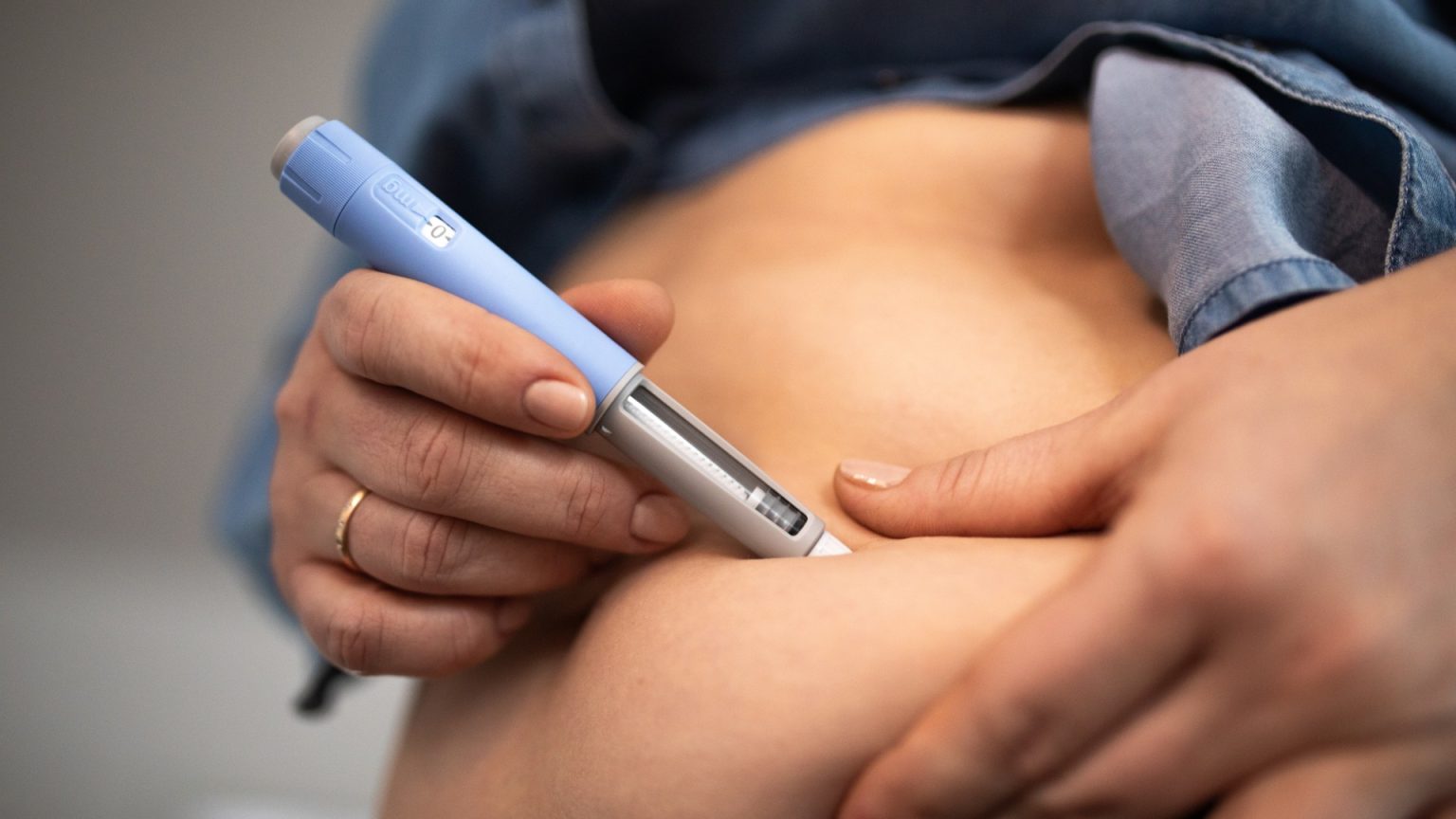
The surging popularity of weight loss injections, specifically GLP-1 receptor agonists like Ozempic and Mounjaro, has prompted extensive research into their comprehensive health impacts. A recent study analyzing the medical records of two million Americans reveals a complex interplay of benefits and risks associated with these drugs. While they demonstrate remarkable efficacy in weight reduction, their influence extends far beyond, affecting a wide spectrum of health conditions. This underscores the need for careful monitoring and informed decision-making when considering these medications for weight management.
The study highlights a significant reduction in the incidence of 42 health conditions among individuals using GLP-1 receptor agonists. These positive effects encompass a range of serious illnesses, including stroke, dementia, various drug addictions, liver cancer, and cardiac arrest. This suggests that these medications may offer substantial protective benefits beyond weight loss, potentially improving overall health and longevity. However, it is crucial to consider these findings in conjunction with the identified risks to gain a balanced perspective.
Conversely, the research also identified an increased risk of 19 other health conditions in individuals using these injections. Among these are arthritis and complications involving the gut, pancreas, and kidneys. Notably, the study revealed a doubled risk of pancreatitis, a potentially life-threatening inflammation of the pancreas, among those taking GLP-1 receptor agonists. This emphasizes the importance of thorough medical evaluation and ongoing monitoring for individuals using these medications, particularly those with pre-existing conditions or risk factors for these complications.
The mechanism of action of GLP-1 receptor agonists involves mimicking a naturally occurring hormone that signals satiety. By slowing down digestion and suppressing cravings, these medications effectively promote weight loss. This mimics the body’s natural response to a full stomach, leading to reduced calorie intake and subsequent weight reduction. This approach has proven highly effective for many individuals struggling with obesity, offering a promising new avenue for weight management.
The growing demand for GLP-1 receptor agonists, with projections of over a million users in the UK alone this year, underscores the need for comprehensive understanding of their long-term effects. The research conducted by Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly at Washington University provides valuable insights into both the benefits and risks, emphasizing the importance of informed decision-making and continuous monitoring for those considering or currently using these medications. Balancing the potential for significant health improvements against the identified risks is crucial for responsible and effective utilization of these powerful drugs.
In conclusion, GLP-1 receptor agonists offer a promising approach to weight management and potentially offer protection against a range of serious health conditions. However, they are not without risks, and careful consideration of both the potential benefits and potential adverse effects is paramount. Continuous monitoring and open communication between patients and healthcare providers are essential for maximizing benefits and minimizing potential harm associated with these medications. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the long-term effects and to identify individuals who are most likely to benefit from these treatments while minimizing risks.