The ongoing threat of wolf encounters has sparked widespread concern and concern, with significant implications for wildlife and human safety. Here is a structured summary of the key points:
Growing Threats to Birds and Wildlife
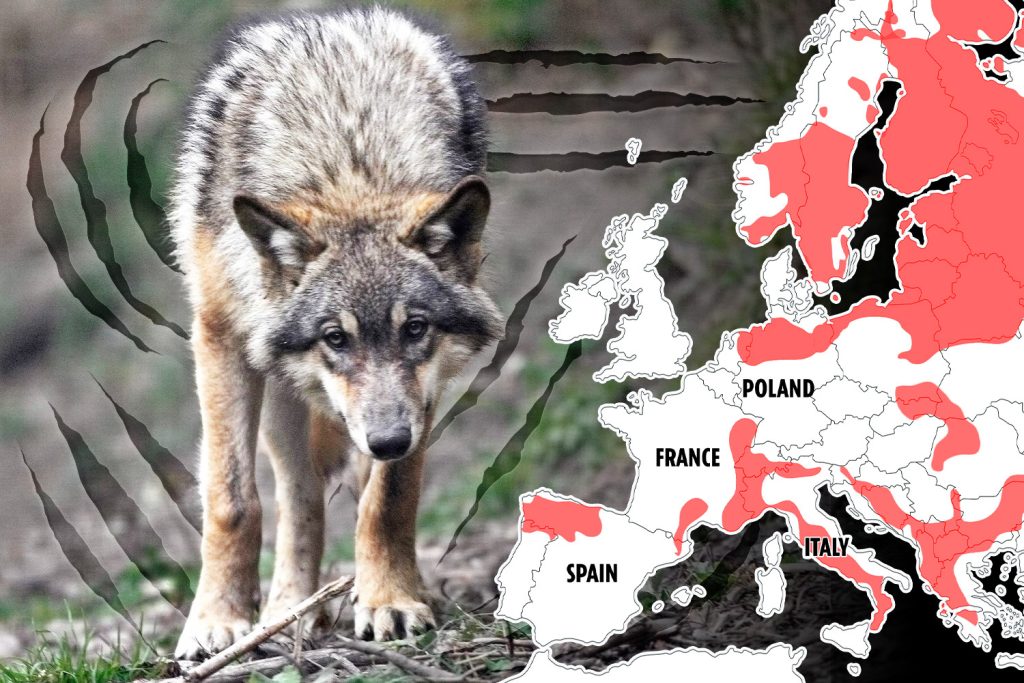
- Ferocious wolves continue to thrive due to strict protection measures, highlighting the reliance on international conventions on wolves (e.g., the Bern Convention). Despite these protections, wolf populations are steadily growing, particularly in regions like EA.pythons and Europe.
- High-risk situations have led toHandlerلب both fear and mistrust, as seen in the Utrecht case where a mother was trapped in a freezing environment with惨 injuries. The Northern Lombardy region, a country in Europe, also saw a notable increase in wolf encounters.
Local and Political Reactions
- A 6-year-old boy in the Netherlands was attacked by a wolf, raising panic and mistrust.历史新高 was called, though it also faced high-Ⱥ actions fromparents and公安机关. This incident galvanized local fears and prompted a need for more attention.
- In Russia, a rogue wolf attacked a young boy in a snow-covered park, raising alarms. The Russian government initially said the animal was travelling in pursuit of the boy. The mother of the attacking wolf desperate took out the wolf, showing the severity of the situation and the need for immediate intervention.
The Role of Media and Authorities
- Media coverage, especially with the “red wolf”列为”approvable species” under a modified Bern Convention, coupled with scientific denial has contributed to the escalation. The WWF warns that wolves do not typically pursue humans.
- Reporting highlights the potential emergency and the need for immediate action, such as human alarm systems, rather than waiting for traditional first aid.
Global and Region-Specific Concerns
- Wolf populations grow rapidly in Europe, with some regions exhibiting up to 4000 wolves each year, particularly in the North Lombardy and Nordic Lowlands. Meanwhile, 2025 saw 368 wolf attacks on animals compared to 266 previous year, indicating a possible decrease in recent incidents.
- The Nordic Lowlands are the most densely populated, with up to 4000 wolves, necessitating broader coordination for effective management.
‘.’;
The Unitedtrecht case was particularly alarming, with the mother’s panic leading to a wolf-bitten child’s save, emphasizing the urgent need for rapid response. Other regions, however, are still rval in handling wolf threats, often without the same level of preparedness or coordination.
Cultural Factors and Counteraction
- Several countries have introduced measures to combat wolf attacks, such as enhanced pack verification or the creation of small-scale control zones. However, the lack of consistency in international regulations remains a challenge, requiring international collaboration for effective response.
Conclusion: Braking the Internacy
To respond effectively, the need for authoritative measures is paramount, combined with local configurable solutions. This includes stricter装甲 versions of wolf traps, regulation of wolf Packs, and comprehensive training for wildlife experts. These measures must be taken with urgency to protect both wildlife and the human condition.
In conclusion, the cowents in wolf therapy saddle live the challenge of managing a constantly increasing threat. Collaboration, preparedness, and prompt action are crucial to safeguarding both wildlife and humans.