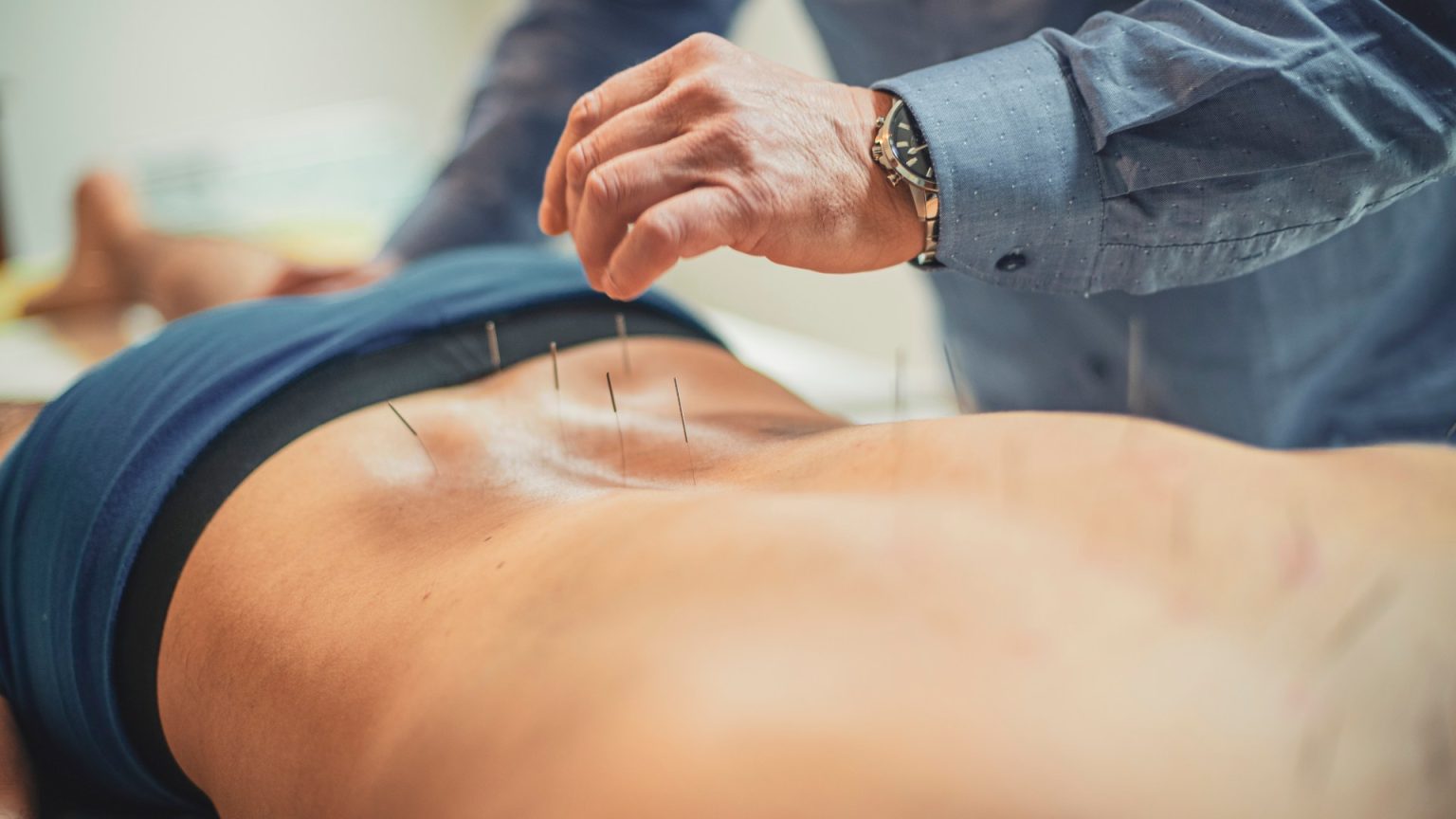
Premature ejaculation (PE) is a common sexual dysfunction affecting a significant portion of the male population, estimated to impact about a third of men, with the prevalence increasing in men over 40. Characterized by the inability to control ejaculation, often occurring within a minute of penetration, PE can lead to significant distress, relationship difficulties, and reduced quality of life for both men and their partners. While various treatment options exist, including pharmacological interventions and behavioral therapies, a recent review of existing research suggests acupuncture may offer a promising alternative approach for managing this condition.
The review, conducted by Dr. Fu Wang and colleagues, analyzed eight previous studies comparing the efficacy of acupuncture to conventional treatments, primarily selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), for PE. The analysis revealed that a consistent regimen of acupuncture sessions, typically lasting 20 to 30 minutes, demonstrably extended the time to ejaculation and enhanced sexual satisfaction for both partners. The acupuncture treatment typically involved inserting needles at specific points, including areas just below the waistband and in the feet, with treatments administered regularly over a period of four to eight weeks. While the research indicated that acupuncture may not be as effective as SSRIs in prolonging ejaculation, it presented a significant advantage: a reduced risk of adverse side effects.
SSRIs, while often effective in delaying ejaculation, can carry a range of potential side effects, including nausea, insomnia, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction. These side effects can deter many men from pursuing this treatment option. Acupuncture, on the other hand, offers a more holistic and minimally invasive approach with a considerably lower risk of adverse reactions. According to Dr. Wang, acupuncture is generally well-tolerated by patients, making it a safer alternative for those hesitant to use pharmaceutical interventions due to concerns about side effects. This provides a valuable alternative for men seeking a natural, low-risk treatment for PE.
The mechanism by which acupuncture improves PE remains incompletely understood, but several theories exist. One hypothesis suggests that acupuncture may regulate hormonal levels, contributing to a more balanced endocrine system and potentially mitigating the physiological factors contributing to premature ejaculation. Another theory posits that acupuncture may dampen the excitability of nerves involved in the ejaculatory reflex, thereby delaying the onset of climax. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the precise mechanisms of action underlying the observed benefits of acupuncture for PE.
The findings of this review are encouraging, suggesting that acupuncture can be a valuable addition to the therapeutic arsenal for managing PE. However, it’s important to note certain limitations. The studies included in the review varied in methodology and sample size, potentially affecting the overall strength of the conclusions. Furthermore, while the review highlights the comparative safety of acupuncture over SSRIs, it’s crucial to recognize that individual responses to treatment can vary, and any therapeutic intervention should be pursued under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional.
In conclusion, premature ejaculation is a common sexual dysfunction that can negatively impact men’s well-being and relationships. Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine therapy, has emerged as a potential alternative treatment option, showing promise in prolonging ejaculation and enhancing sexual satisfaction. While further research is necessary to solidify these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms, the current evidence suggests that acupuncture can be a safe and effective approach for men seeking a non-pharmacological solution for PE, especially for those concerned about the potential side effects of conventional medications. Consulting with a qualified healthcare practitioner is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment strategy based on individual needs and circumstances.